Primary Region and Read Regions
The Upstash Global database is structured with a Primary Region and multiple Read Regions. When a write command is issued, it is initially sent and processed at the Primary Region. The write operation is then replicated to all the Read Regions, ensuring data consistency across the database. On the other hand, when a read command is executed, it is directed to the nearest Read Region to optimize response time. By leveraging the Global database’s distributed architecture, read operations can be performed with reduced latency, as data retrieval occurs from the closest available Read Region. The Global database’s design thus aids in minimizing read operation latency by efficiently distributing data across multiple regions and enabling requests to be processed from the nearest Read Region. User selects a single primary region and multiple read regions. For the best performance, you should select the primary region in the same location where your writes happen. Select the read regions where your clients that read the Redis located. You may have your database with a single primary region but no read regions which would be practically same with a single region (regional) database. You can add or remove regions on a running Redis database. Here the list of regions currently supported:- AWS US-East-1 North Virginia
- AWS US-West-1 North California
- AWS US-West-2 Oregon
- AWS EU-West-1 Ireland
- AWS EU-Central-1 Frankfurt
- AWS AP-SouthEast-1 Singapore
- AWS AP-SouthEast-2 Sydney
- AWS SA-East-1 São Paulo
- Read latency from the same region <1ms
- Write latency from the same region <5ms
- Read/write latency from the same continent <50ms
Architecture
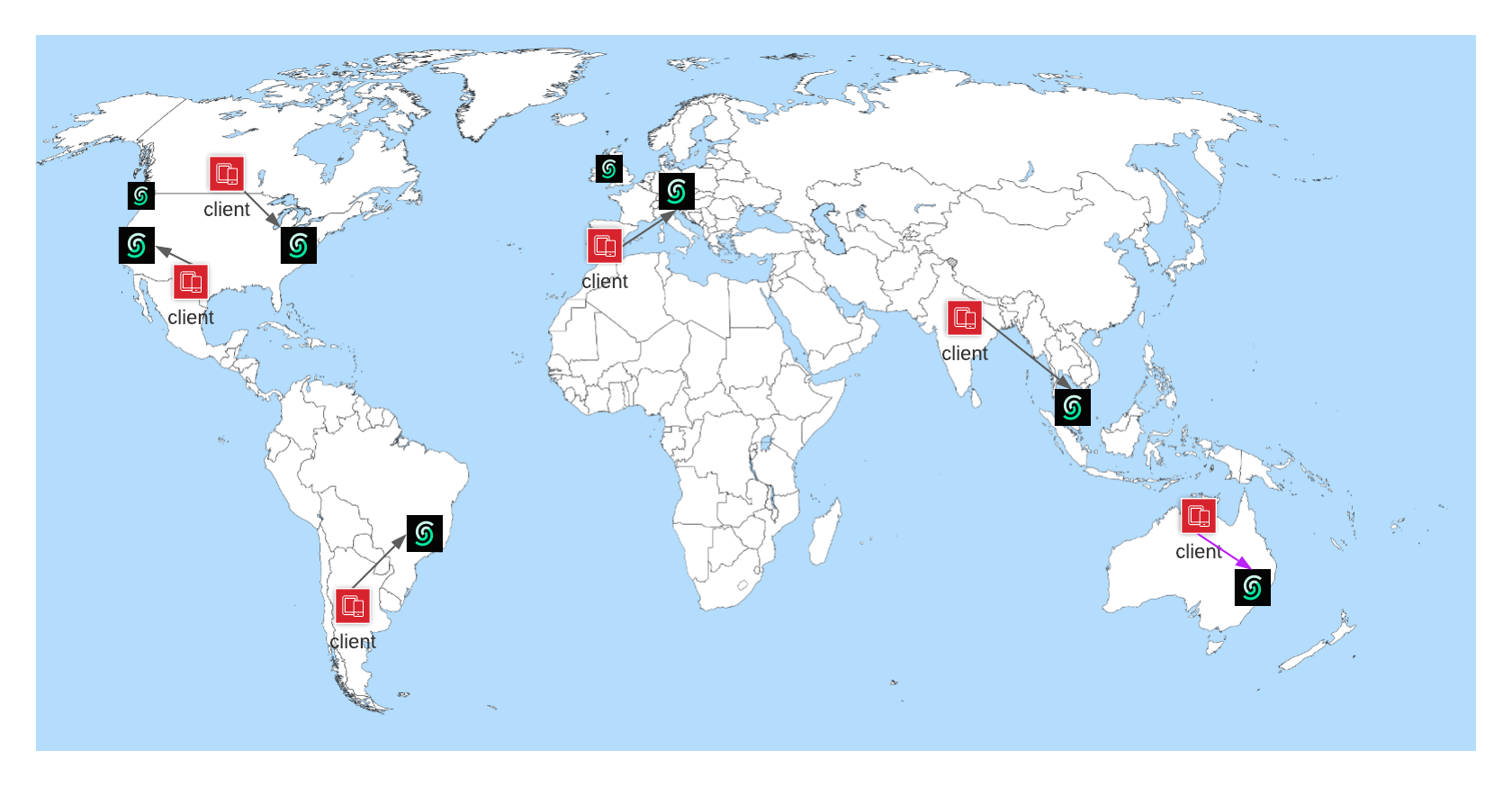
In the multi region architecture, each key is owned by a primary replica which is located at the region that you choose as primary region. Read replicas become the backups of the primary for the related keys. The primary replica processes the writes, then propagates them to the read replicas. Read requests are processed by all replicas, this means you can read a value from any of the replicas. This model gives a better write consistency and read scalability. Each replica employs a failure detector to track the liveness of the primary replica. When the primary replica fails for a reason, read replicas start a new leader election round and elect a new leader (primary). This is the only unavailability window for the cluster where your requests can be blocked for a short period of time.Global Database is designed to optimize the latency of READ operations. It may
not be a good choice if your use case is WRITE heavy.
Use Cases
- Edge functions: Edge computing (Cloudflare workers, Fastly Compute) is becoming a popular way of building globally fast applications. But there are limited data solutions accessible from edge functions. Upstash Global Database is accessible from Edge functions with the REST API. Low latency from all edge locations makes it a perfect solution for Edge functions
- Multi region serverless architectures: You can run your AWS Lambda function in multiple regions to lower global latency. Vercel/Netlify functions can be run in different regions. Upstash Global database provides low latency data wherever your serverless functions are.
- Web/mobile use cases where you need low latency globally. Thanks to the read only REST API, you can access Redis from your web/mobile application directly. In such a case, Global Database will help to lower the latency as you can expect the clients from anywhere.

